| February 8-February 12: Action Potential (AP), AP Transmission into Skeletal Muscle, Muscle Contraction, Physiology of Hypertrophy, Science in the Classroom OBJECTIVES: Be able to explain in detail the steps of an Action Potential (AP) Be able to explain the mechanisms of the sodium-potassium pump Be able to describe the updated physiological steps of the arrival of a nerve impulse at the neuromuscular junction and transmission of AP into muscle Be able to discuss the physiological hypertrophic factors in muscle from resistance exercise Be able to discuss some science updates in reference to muscle physiology Please note there are FOUR YOUTUBE videos with this week's lessons. Click Here to Download Exam 1 Part D due Friday February 12 by 12 Midnight Let's start this section by watching this Youtube Video on the Action Potential Part 1 Click here to watch the Action Potential Part 1YOUTUBE video Let's Review, from all the YOUTIBE Videos, a few questions and concepts: What researchers are recognized with explaining the action potential? (Andrew Huxley and Alan Hodgkin) What part of the motor neuron receives sensory stimuli? (dendrites) What part of the motor neuron processes incoming stimuli to determine whether to send an excitatory or inhibitory message? (axon hillock) The axon is surrounded by an insulation referred to as the_______ ? (myelin sheath) The myelin sheath is made of __________cells? (Schwann) The propagation (or spread) of the action potential is referred to as a ____________ conduction? (saltatory) How fast is the propagation of the nerve impulse along the axon? (100 meters/sec) What ion is predominantly intracellular at RMP (rest)? (potassium) What ion is predominantly extracellular at RMP (rest)? (sodiim) A graded potential that is more negative at RMP (rest) is called a ____________? (hyperpolarizatoin) A graded potential that is more positive at RMP (rest) is called a ____________? (depolarization) Threshold for a nerve is met at what mV ____________? (55 mV) A nerve that has met threshold will spike to what mV ____________? (+30 mV) The sodium potassium pump does it work by Active Transport. The means it requires_____? (ATP) What medical doctor who discovered animal electricity? (Luigi Galvani, MD) What is a ligand? (A molecule that binds anoher molecule) What ion channel on the motor endplate is a ligand-gated ion channel? (the ACh receptor molecule that binds with ACh) From the YOUTUBE video on Science in the Classroom, what muscle protein is very involved in eccentric muscle actins? (Titin) |
||||||||
| Click here to watch the Action Potential Part 2 YOUTUBE video | ||||||||
| Action Potential Mechanisms | ||||||||
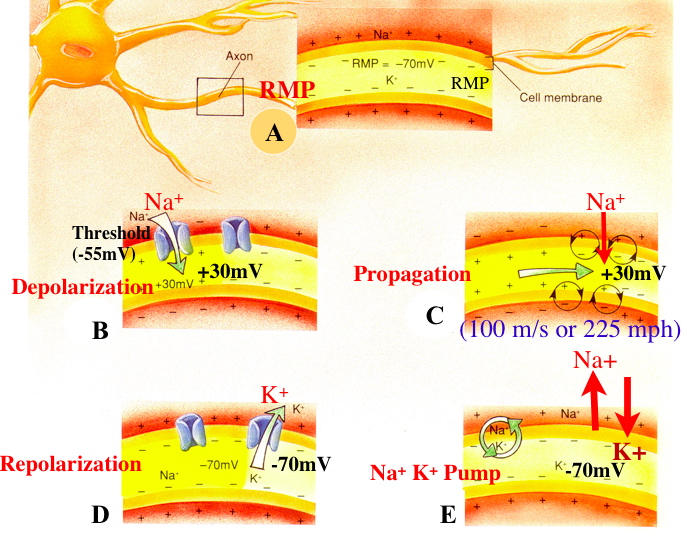 |
||||||||
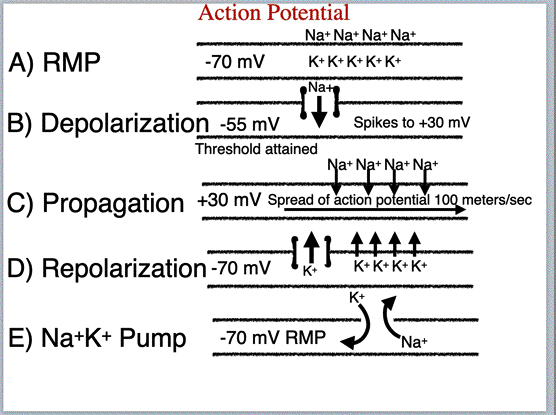 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Sodium Postasium Pump and Node of Ranvier Mechanisms | ||||||||
| Click here to watch the Action Potential Part 3 YOUTUBE video | ||||||||
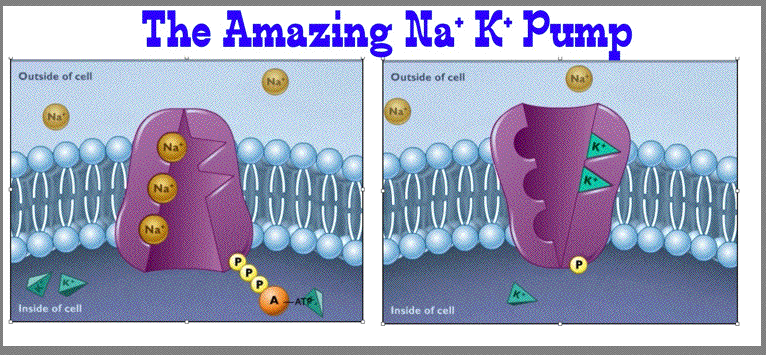 |
||||||||
| Question: How does the Sodium Postassium Pump help to create the -70mV RMP charge of the nerve cell? (Answer: By pumping 3 molecules of sodium extracellular to the two molecules of postassium intracellular the pump is creating a voltage difference across the membrane. The inside of the cell is negative in reference to the positive outside of the cell.) | ||||||||
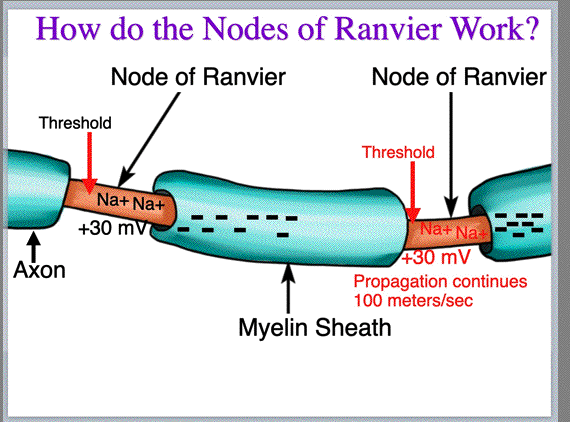 |
||||||||
| After watching the Youtube Video please explain how the action potential spreads from Node of Ranvier to Node of Ranvier? (Answer: when the threshold is met at one Node of Ranvier the charge spikes to +30 mV from the rush of Na+ through the Na+ voltage-gated ion channels. In biochemistry, opposite charges attrack. The +30mV charge draws a lot of ions with negative charges toward it. This causes a depolarization at the next Node of Ranvier to reach threshold, opening Na+ voltage-gated ion channels. Here again the Node of Ranvier spikes to +30mV. This draws ions with negative charges towards it and another depolarization occurs at the next Node of Ranvier. This propagation continues along the axon at 100 meters/sec. Note, depolarization means loss of negative charge and that is precisely what is happening at each Node of Ranvier as it attains threshold.) | ||||||||
| The Steps of the Action Potential into Muscle Contraction | ||||||||
| PRACTICE QUIZ OF COMPLETE MUSCLE CONTRACTION FROM ARRIVAL OF ACTION POTENTIAL: TRY PRINTING THIS PAGE AND THEN NUMBER THE SEQUENCE IN CORRECT ORDER. CHECK YOUR ANSWERS BELOW: ____Calcium ions released from SR ____Calcium ions rush in and react with synapsin on synaptic vesicles ____Myosin (S1 units) combine with actin ____With ATP present, ATPase splits ATP to ADP + Pi + Energy ____Tropomyosin returns over active sites on actin and contraction ceases ____Impulse travels T- tubules & excites sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) ____Motor nerve’s impulse action potential arrives at axon terminal of the neuromuscular junction ____Shift of tropomyosin, make sites available for myosin ____Acetylcholine released via process of exocytosis ____Calcium binds with troponin ____Sliding action of actin over myosin (Power Stroke) ____Acetylcholine binds with receptor sites on motor end plate causing depolarization of motor end plate and sarcolemma (AChE repackages ACh back into synaptic vesicles) ____Impulse stops to muscle: calcium ions pumped back into sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) ____Synaptic vesicles fuse with cell membrane |
||||||||
| Click here to watch the Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Science in the Classroom YOUTUBE video | ||||||||
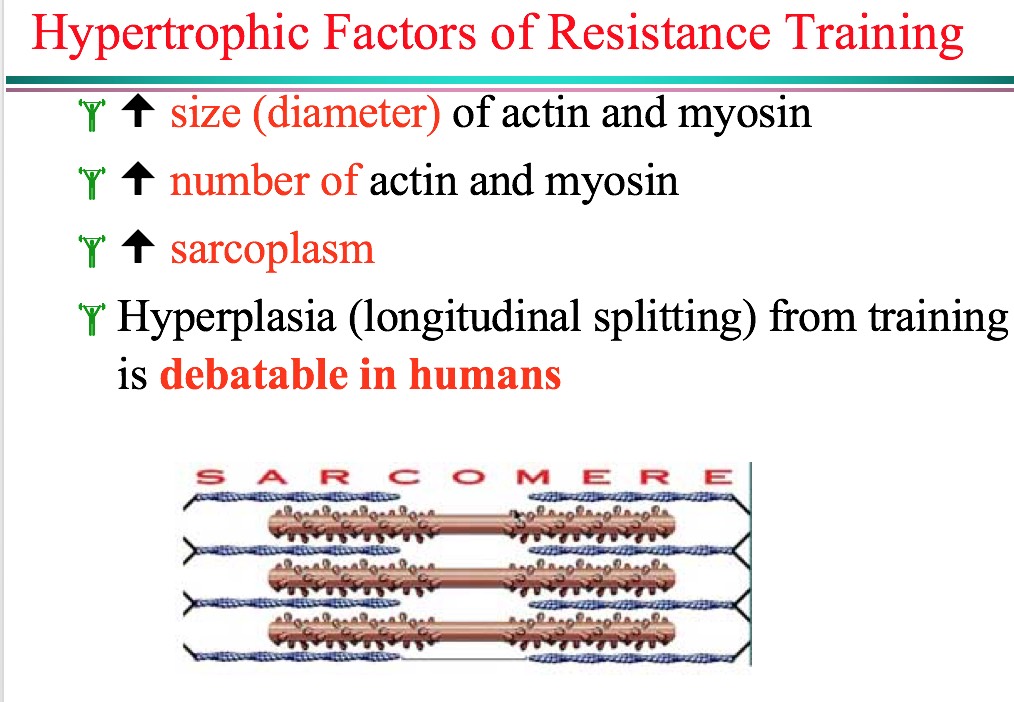 |
||||||||
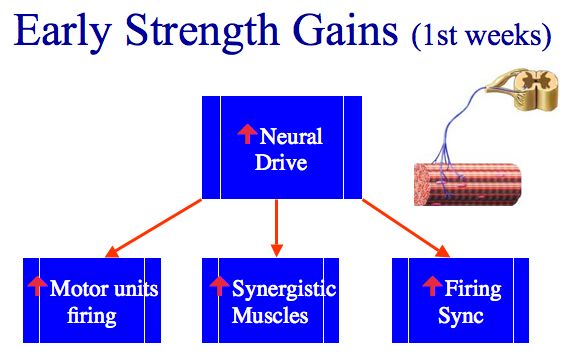 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Check Your Answers: QUIZ OF COMPLETE MUSCLE CONTRACTION FROM ARRIVAL OF ACTION POTENTIAL! 7—Calcium ions released from SR |
||||||||
|